Activity 1
Essential Question
- How does due process protect the rights of individuals?
Background
Due process guarantees equality in the eyes of the law and ensures fair treatment from the federal and state governments.

Instructional Strategies
Strategy 1 |
Think/Pair/Share
Brainstorm with students about “fairness.” Provide each student with a handout of the following questions:
If you are accused of something, which is fairer?
-
- for you to be present when the accusation is made?
- for you to be unaware that you are being accused?
Is it unfair to ask you a question if the answer could show you are guilty of doing something wrong? Why or why not?
Can you remember a situation in which to be fair you needed a friend, parent, a teacher or someone else to stand up for you?
Do you think it is unfair to accuse someone of doing something wrong based upon his/her reputation?
Example: Someone had previously been caught stealing from classmates and arrested for shoplifting, would it be fair to assume that this person is automatically the one in his group that committed a theft?
Is it fair to be told you are being punished for something without any warning or without giving you an opportunity to explain yourself? Why or why not?
Divide students into groups of four or five. Each group should create a list of fair rights for public school students. Have them write their lists on chart paper. Ask each group to share and explain their list to the entire class.
Ask students to Think/Pair/Share about the meaning of the term due process in the United States Constitution. Explain to students that fairness is an important part of our Constitutional rights. Assign readings from a text or other source that explains more about due process and the Fourth, Fifth, Sixth, Eighth and Fourteenth Amendments.
Check for Understanding
- How does our Constitution guarantee that we will be treated fairly by our government? Why is this important to you as an individual?
Strategy 2 |
Concept Formation
Using the following websites, have students work in groups to find three definitions for each concept:
- Habeas Corpus
- Right Against Self-Incrimination
- Right to Counsel
- Presumption of Innocence
- Trial by jury
- Double Jeopardy
- Notice
- Right of Appeal
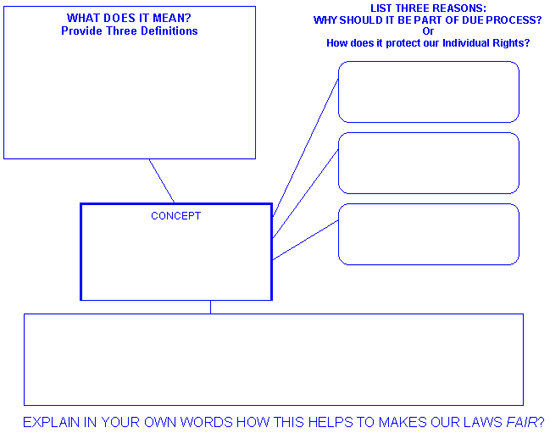
Explain that the Fifth and Fourteenth Amendments protect these rights. Connect this discussion to prior knowledge- questions from the previous activity.
Use a transparency to show a blank Concept of Definition Map. Explain how a Concept of Definition Map works and how it helps us to better understand concepts like those we have just researched. Have each group complete a transparency with a blank Concept of Definition Map on it. Have each group share there map with the class.
Use the completed Concept of Definition Map to summarize the discussion and to ensure that accurate information goes into student notebooks. Review what they have discovered about the meaning and importance of each the concepts.
Check for Understanding |
Printable Student View |
| The district attorney had to press charges or let the prisoner go. | a. Presumption of Innocence | |
| O. J. Simpson will never be tried for the murder of his ex-wife again. | b. Right of Appeal | |
| The attorney explained to his client that the burden of proof was not his and that there wasn’t enough evidence to convict him beyond a reasonable doubt. | c. Trial by Jury | |
| The decision of whether or not the accused was guilty or innocent would be up to a group of his peers. | d. Habeas Corpus | |
| The defense attorney asked that the trial be delayed so that he would have time to prepare a defense. | e. Right Against Self- Incrimination | |
| Many people wondered if Martha would take the court’s decision for review by a higher court. | f. Right to Counsel | |
| The accused was poor so the judge asked if he wanted a public defender. | g. Notice | |
| As the young woman was being handcuffed, the policeman stated “You have a right to remain silent . . .” | h. Double Jeopardy |
Strategy 3 |
Graphic Organizer: Inquiry Chart
Use the website www.usconstitution.net/consttop_duep.html to answer this question:
- Before, during and after completing their internet search, tell students to answer the following questions by completing the Inquiry Chart that asks:
- Are teachers principals and other school officials required to provide due process rights to students?
- How does the phrase from the Fourteenth Amendment: “nor shall any State deprive any person of life, liberty, or property, without due process of law” apply to public school students?
- Are public school students protected from corporal punishment (spanking) for breaking school rules according to the Eighth Amendment’s protection from cruel and unusual punishment?
INQUIRY CHART
|
TOPIC: Due Process Rights of Public School Students |
1. Are teachers, principals, and other school officials required to provide due process rights to students? | 2. How does the phrase from the Fourteenth Amendment: “nor shall any State deprive any person of life, liberty, or property, without due process of law” apply to public school students? | 3. Are public school students protected from corporal punishment (spanking) for breaking school rules according to the Eighth Amendment’s protection from cruel and unusual punishment? |
|
WHAT DO I (WE) ALREADY KNOW?
|
|||
|
WHAT QUESTIONS DO I (WE) HAVE?
|
|||
| WEB SOURCE 1:
|
|||
| WEB SOURCE 2:
|
|||
| WEB SOURCE 3:
|
Check for Understanding |
Printable Student View |
Answer the following questions:
- Why are teachers and other school officials required to give students due process rights?
- Can a students be suspended without due process for threatening a teacher or other student?
- Is the use of corporal punishment against a students’ Constitutional Due Process Rights?