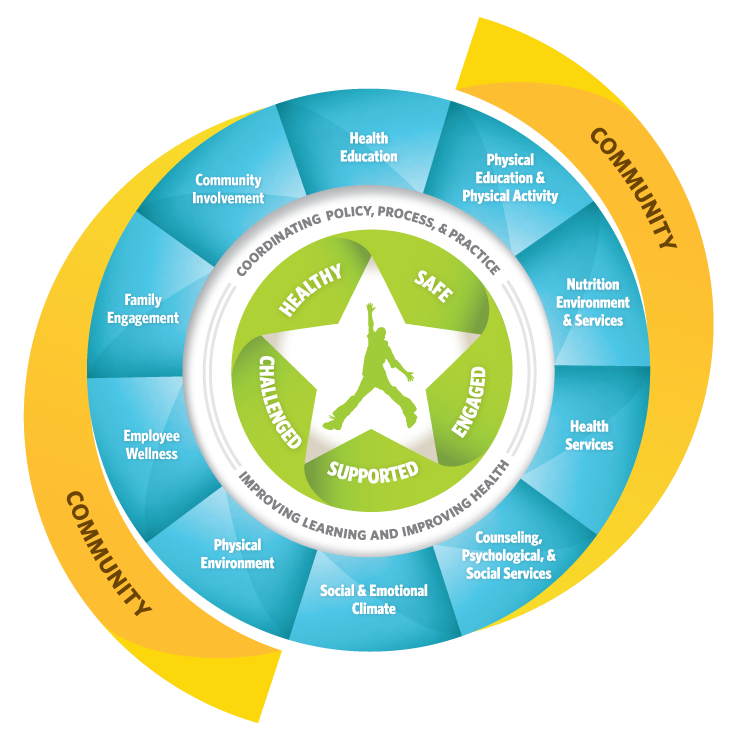
The Whole School, Whole Community, Whole Child (WSCC) Model, formerly known as a Coordinated School Health Program (CSHP), consists of ten interactive components. Schools by themselves cannot, and should not be expected to address the nation’s most serious health and social problems. Families, health care workers, the media, religious organizations, community organizations that serve youth and young people themselves also must be systematically involved. However, schools could provide a critical facility in which many agencies might work together to maintain the well-being of young people.
A planned, sequential, K – 12 curriculum that addresses the physical, mental, emotional and social dimensions of health. The curriculum is designed to motivate and assist students to maintain and improve their health, prevent disease, and reduce health-related risk behaviors. It allows students to develop and demonstrate increasingly sophisticated health-related knowledge, attitudes, skills, and practices. The comprehensive health education curriculum includes a variety of topics such as personal health, family health, community health, consumer healthy, environmental health, sexuality education, mental and emotional health, injury prevention and safety, nutrition, prevention and control of disease, and substance use and abuse. Qualified, trained teachers provide health education.
2. Physical Education & Physical Activity
Schools can create an environment that offers many opportunities for students to be physically active throughout the school day. A comprehensive school physical activity program (CSPAP) is the national framework for physical education and youth physical activity. A CSPAP reflects strong coordination across five components: physical education, physical activity during school, physical activity before and after school, staff involvement, and family and community engagement. Physical education serves as the foundation of a CSPAP and is an academic subject characterized by a planned, sequential K-12 curriculum that is based on the national and/or state standards for physical education. Physical education provides cognitive content and instruction designed to develop motor skills, knowledge, and behaviors for healthy active living, physical fitness, sportsmanship, self-efficacy, and emotional intelligence. A well-designed physical education program provides the opportunity for students to learn key concepts and practice critical skills needed to establish and maintain physically active lifestyles throughout childhood, adolescence and into adulthood. Teachers should be certified or licensed, and endorsed by the state to teach physical education.
School health services intervene with actual and potential health problems, including providing first aid, emergency care and assessment and planning for the management of chronic conditions (such as asthma or diabetes). In addition, wellness promotion, preventive services and staff, student and parent education complement the provision of care coordination services. These services are also designed to ensure access and/or referrals to the medical home or private healthcare provider. Health services connect school staff, students, families, community and healthcare providers to promote the health care of students and a healthy and safe school environment. School health services actively collaborate with school and community support services to increase the ability of students and families to adapt to health and social stressors, such as chronic health conditions or social and economic barriers to health, and to be able to manage these stressors and advocate for their own health and learning needs. Qualified professionals such as school nurses, nurse practitioners, dentists, health educators, physicians, physician assistants and allied health personnel provide these services.
Access to a variety of nutritious and appealing meals that accommodate the health and nutrition needs of all students. School nutrition programs reflect the U.S. Dietary Guidelines for Americans and other criteria to achieve nutrition integrity. The school nutrition services offer students a learning laboratory for classroom nutrition and health education, and serve as a resource for linkages with nutrition-related community services. Qualified child nutrition professionals provide these services.
5. Counseling, Psychological & Social Services
These prevention and intervention services support the mental, behavioral, and social-emotional health of students and promote success in the learning process. Services include psychological, psychoeducational, and psychosocial assessments; direct and indirect interventions to address psychological, academic, and social barriers to learning, such as individual or group counseling and consultation; and referrals to school and community support services as needed. Additionally, systems-level assessment, prevention, intervention, and program design by school-employed mental health professionals contribute to the mental and behavioral health of students as well as to the health of the school environment. These can be done through resource identification and needs assessments, school-community-family collaboration, and ongoing participation in school safety and crisis response efforts. Additionally, school-employed professionals can provide skilled consultation with other school staff and community resources and community providers. School-employed mental health professionals ensure that services provided in school reinforce learning and help to align interventions provided by community providers with the school environment. Professionals such as certified school counselors, school psychologists, and school social workers provide these services.
A healthy and safe physical school environment promotes learning by ensuring the health and safety of students and staff. The physical school environment encompasses the school building and its contents, the land on which the school is located, and the area surrounding it. A healthy school environment will address a school’s physical condition during normal operation as well as during renovation (e.g., ventilation, moisture, temperature, noise, and natural and artificial lighting), and protect occupants from physical threats (e.g., crime, violence, traffic, and injuries) and biological and chemical agents in the air, water, or soil as well as those purposefully brought into the school (e.g., pollution, mold, hazardous materials, pesticides, and cleaning agents).
Opportunities for school staff to improve their health status through activities such as health assessments, healthy education and health-related fitness activities. These opportunities encourage school staff to pursue a healthy lifestyle that contributes to their improved health status, improved morale, and a greater personal commitment to the school’s overall coordinated health program. This personal commitment often transfers into greater commitment to the health of students and creates positive role modeling. Health promotion activities have improved productivity, decreased absenteeism, and reduced health insurance costs.
Families and school staff work together to support and improve the learning, development, and health of students. Family engagement with schools is a shared responsibility of both school staff and families. School staff are committed to making families feel welcomed, engaging families in a variety of meaningful ways, and sustaining family engagement. Families are committed to actively supporting their child’s learning and development. This relationship between school staff and families cuts across and reinforces student health and learning in multiple settings—at home, in school, in out-of-school programs, and in the community. Family engagement should be continuous across a child’s life and requires an ongoing commitment as children mature into young adulthood.
Community groups, organizations, and local businesses create partnerships with schools, share resources, and volunteer to support student learning, development, and health-related activities. The school, its students, and their families benefit when leaders and staff at the district or school solicits and coordinates information, resources, and services available from community-based organizations, businesses, cultural and civic organizations, social service agencies, faith-based organizations, health clinics, colleges and universities, and other community groups. Schools, students, and their families can contribute to the community through service-learning opportunities and by sharing school facilities with community members (e.g., school-based community health centers and fitness facilities).
10. Social and Emotional Climate
Social and Emotional School Climate refers to the psychosocial aspects of students’ educational experience that influence their social and emotional development. The social and emotional climate of a school can impact student engagement in school activities; relationships with other students, staff, family, and community; and academic performance. A positive social and emotional school climate is conducive to effective teaching and learning. Such climates promote health, growth, and development by providing a safe and supportive learning environment.